Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms, Causes, Pain, Meaning, Treatment Myth and Fact
Introduction to Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy, a term that many might have heard but few fully understand. So, what exactly is it? Simply put, an ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg implants itself outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes. This can be a life-threatening condition that needs urgent medical attention. Let’s explore this important medical issue in more detail.
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
In a normal pregnancy, the fertilized egg travels down the fallopian tube and implants itself in the uterus, where it grows into a baby. In an ectopic pregnancy, however, the egg implants outside the uterus. This typically happens in a fallopian tube, but it can also occur in the abdominal cavity, ovary, or cervix.
Normal vs. Ectopic Pregnancy
In a healthy pregnancy, the egg smoothly travels from fertilization to implantation in the uterus. But in an ectopic pregnancy, this journey is disrupted, causing the egg to implant in areas where it can’t develop properly.
Common Sites of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Fallopian Tubes: The most common site.
- Abdominal Cavity: Rare but possible.
- Ovary: Occasionally, the egg implants here.
- Cervix: The least common site.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
Understanding the causes of ectopic pregnancy can help in its prevention and early detection.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy:
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: Increases the likelihood of recurrence.
- Inflammation or Infection: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can cause damage to the fallopian tubes.
- Fertility Treatments: Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) may increase the risk.
- Tubal Surgery: Any surgery on the fallopian tubes can result in scarring.
- Smoking: Smokers have a higher risk compared to non-smokers.
Medical Conditions
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Can cause scarring in the fallopian tubes.
- Endometriosis: The growth of uterine tissue outside the uterus can affect the fallopian tubes.
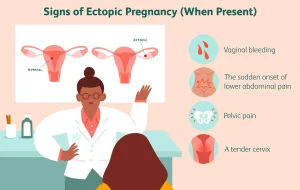
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Early detection is crucial for managing an ectopic pregnancy effectively.
Early Signs
- Light Vaginal Bleeding: Often mistaken for a normal period.
- Pelvic Pain: Usually on one side of the abdomen.
- Shoulder Pain: Caused by internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm.
Severe Symptoms
- Heavy Bleeding: Can indicate a ruptured fallopian tube.
- Severe Abdominal Pain: A sign of a medical emergency.
- Fainting or Dizziness: Due to internal bleeding and low blood pressure.
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Accurate diagnosis is essential for appropriate treatment.
Medical History and Physical Exam
Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound: Transvaginal ultrasound is used to locate the pregnancy.
- MRI: In rare cases, MRI may be used for detailed imaging.
Blood Tests
- hCG Levels: Lower than normal hCG levels can indicate an ectopic pregnancy.
- Progesterone Levels: Low levels can support the diagnosis.
Types of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies can occur in different locations, each with unique challenges.
Tubal Pregnancy
The most common type, occurring in the fallopian tubes.
Non-Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy
- Abdominal Pregnancy: Implantation in the abdominal cavity.
- Ovarian Pregnancy: Egg implants in the ovary.
- Cervical Pregnancy: Implantation in the cervix.
Complications of Ectopic Pregnancy
If not treated promptly, ectopic pregnancy can lead to severe complications.
Internal Bleeding
A ruptured fallopian tube can cause severe internal bleeding, which may lead to shock.
Infertility Issues
Damage to the fallopian tubes can affect future fertility.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies depending on the severity and location of the ectopic pregnancy.
Medication
- Methotrexate is a medication that halts the growth of pregnancy tissue.
Surgery
-
- Laparotomy: Open surgery in more severe cases.
Expectant Management
In rare cases, if the pregnancy is very early and hCG levels are decreasing, careful monitoring may be chosen.
Recovery and Aftercare
Physical Recovery
- Rest and Hydration: Essential for physical healing.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Necessary to ensure complete recovery.
Emotional Support
- Counseling: Professional help to cope with the emotional impact.
-
Prevention of Ectopic Pregnancy
While not all cases can be prevented, some steps can reduce the risk.
Reducing Risk Factors
- Quit Smoking: Reduces the risk significantly.
- Treating Infections: Early treatment of STIs to prevent tubal damage.
Regular Medical Checkups
Regular visits to your gynecologist can help in early detection and treatment of conditions that might lead to an ectopic pregnancy.
Living with a History of Ectopic Pregnancy
Having had an ectopic pregnancy can affect future pregnancies and overall health.
Future Pregnancy Plans
- Consult Your Doctor: Prior to attempting conception again.
- Regular Monitoring: Early ultrasounds in future pregnancies.
Support Groups and Counseling
Engaging with support groups can provide comfort and understanding.
Myths and Facts about Ectopic Pregnancy
Let’s clear up some common misconceptions.
Common Misconceptions
- Myth: Ectopic pregnancies are caused by lifting heavy objects.
- Fact: They are usually due to issues within the reproductive system.
Verified Information
- Fact: Ectopic pregnancy can occur even if you’ve never had a previous one.
- Fact: Early treatment can save lives and preserve fertility.
Case Studies
Real-life stories can provide valuable insights and lessons.
Real-Life Experiences
Sharing experiences of those who have gone through ectopic pregnancy.
Lessons Learned
Understanding the importance of early detection and prompt treatment.
20 FAQs on Ectopic Pregnancy
1. What is an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tubes. This is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment.
2. What are the main symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy?
Early symptoms include light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain. Severe symptoms may include heavy bleeding, severe abdominal pain, and dizziness.
3. What causes an ectopic pregnancy?
Causes can include damage to the fallopian tubes from previous infections or surgeries, hormonal imbalances, and abnormal development of the fertilized egg.
4. How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, ultrasound imaging, and blood tests to measure hormone levels.
5. Can an ectopic pregnancy be treated with medication?
Yes, in some cases, medication such as methotrexate is used to stop the growth of the pregnancy tissue.
6. What surgical options are available for ectopic pregnancy?
Surgical treatments include laparoscopy to remove the ectopic pregnancy or, in severe cases, laparotomy, an open surgery.
7. Is it possible to have a normal pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy?
Yes, many women can have normal pregnancies after an ectopic pregnancy, although they may be at higher risk and require close monitoring.
8. What are the risk factors for an ectopic pregnancy?
Risk factors include previous ectopic pregnancies, pelvic inflammatory disease, fertility treatments, smoking, and tubal surgery.
9. How common is ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancies occur in about 1-2%
10. What are the complications of an untreated ectopic pregnancy?
Untreated ectopic pregnancy can lead to life-threatening internal bleeding and damage to the fallopian tubes, which can affect future fertility.
11. Can an ectopic pregnancy resolve on its own?
In very rare cases, an ectopic pregnancy may resolve without intervention, but medical supervision is essential.
12. What long-term effects can result from an ectopic pregnancy?
Long-term effects may include damage to the fallopian tubes, affecting fertility and increasing the risk of future ectopic pregnancies.
13. How soon can I try to conceive after an ectopic pregnancy?
It is generally recommended to wait at least 3-6 months before trying to conceive again, and always consult with your doctor.
14. Are there support groups for women who have had an ectopic pregnancy?
Yes, there are many support groups and counseling services available for women who have experienced an ectopic pregnancy.
15. What should I do if I suspect an ectopic pregnancy?
Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect an ectopic pregnancy. Early detection and treatment are critical.
16. Is there a way to prevent an ectopic pregnancy?
While not all cases can be prevented, reducing risk factors such as quitting smoking and treating infections promptly can help.
17. How does an ectopic pregnancy affect future pregnancies?
Having had an ectopic pregnancy may increase the risk of future ectopic pregnancies, but many women still go on to have healthy pregnancies.
18. Can ectopic pregnancy be detected early?
Yes, with regular medical checkups and monitoring, an ectopic pregnancy can often be detected early, which is crucial for treatment.
19. What role do hormonal levels play in diagnosing ectopic pregnancy?
Abnormal levels of hCG and progesterone can indicate an ectopic pregnancy, as they differ from levels seen in a normal pregnancy.
20. What is the prognosis for women after treatment for an ectopic pregnancy?
With prompt and appropriate treatment, most women recover well and can have successful pregnancies in the future, though close medical monitoring is advised.